Why would I assign Autoscale policies to a server?
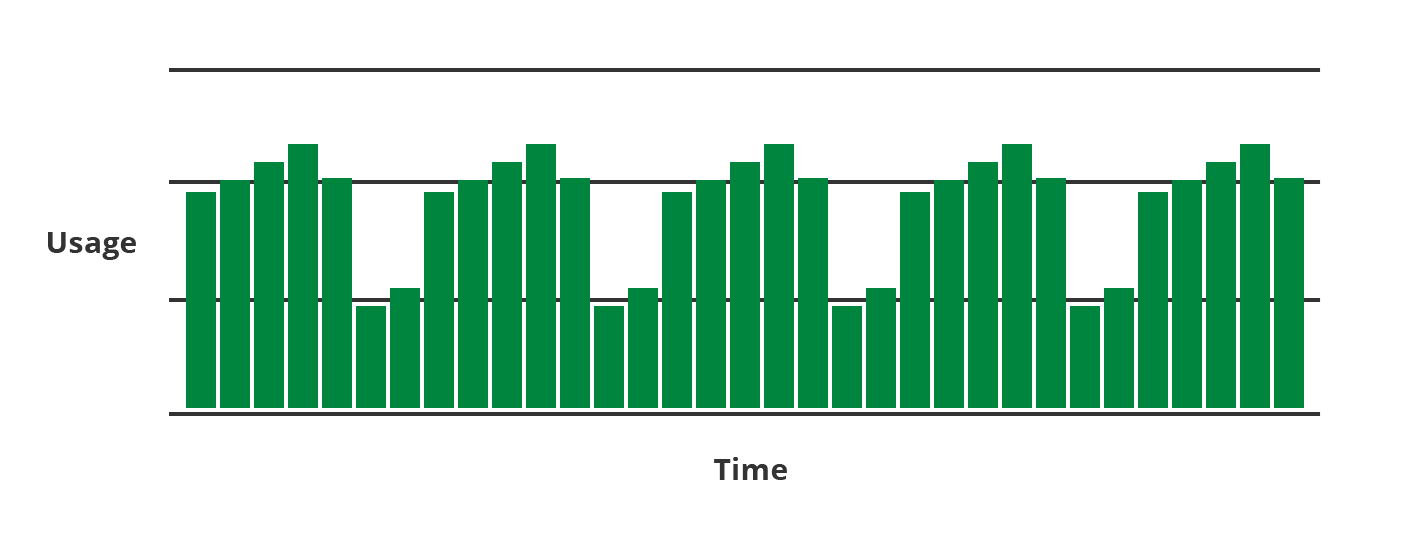
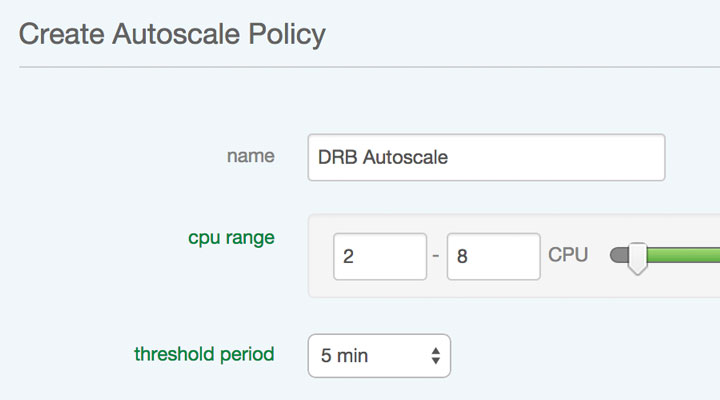
Autoscale makes it possible for a server or group of servers to self-regulate and only have the capacity it needs at any given time, based on real-world usage. This saves you money while reducing administrative overhead. Instead of having a system administrator closely monitor and scale servers based on an increase or decrease in utilization, you can create policies that add or remove capacity automatically. This ensures that you don't have CPUs allocated or additional servers powered on (costing you money!) unless you need them.
When should I use horizontal Autoscale vs. vertical Autoscale?
Many enterprise workloads can see an increase in performance just by adding capacity to existing servers without the need for additional servers. This is often the case if the workload is purely CPU-constrained and not I/O bound. For these types of workloads, vertical Autoscale may prove to be enough. If you find that your workload has very large spikes that require bigger bursts than vertical Autoscale may be able to provide, horizontal Autoscale is definitely a powerful option as well. You can always start out using vertical Autoscale, and later change to using a horizontal Autoscale policy instead, if you determine that it isn't enough for you. Or, if you know your workload causes your servers to become I/O bound, you may want to use horizontal Autoscale from the start. Also, horizontal Autoscale relies on load balancers to scale the workload. If you have a workload that doesn't scale out well this way (i.e. database servers), vertical Autoscale is the better bet. Conversely, the web tier is a great candidate for horizontal Autoscale as it scales out behind a load balancer well.
What Operating Systems support Autoscale?
Vertical Autoscale can be applied to any server type that supports a "hot add" of CPU resources without a reboot. Those OSs include: Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 or 6, and Ubuntu 10 or 12 x64. Horizontal Autoscale is applied at the group level and will work with any server types within that group.
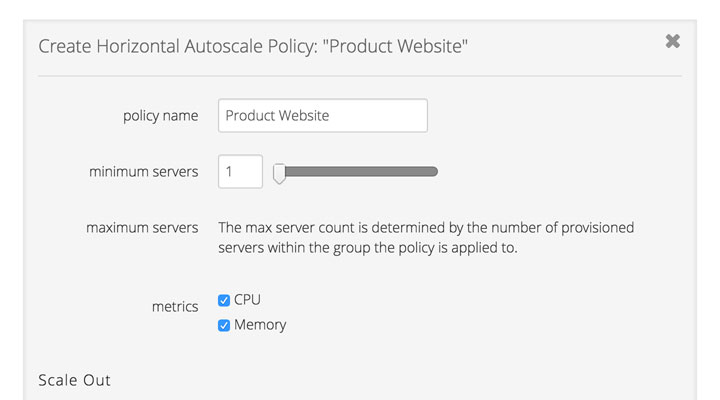
What's the difference between horizontal and vertical Autoscale policies?
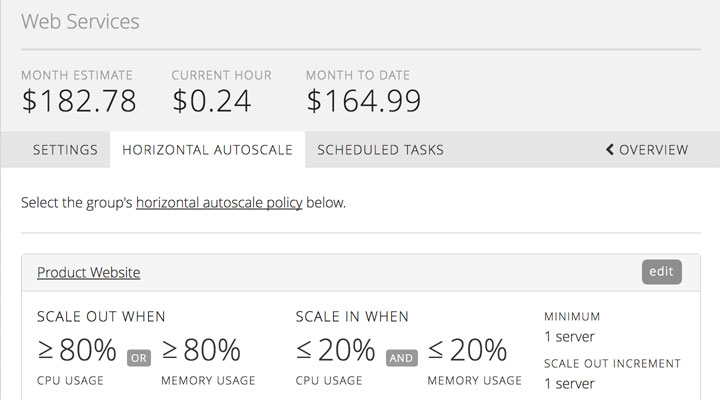
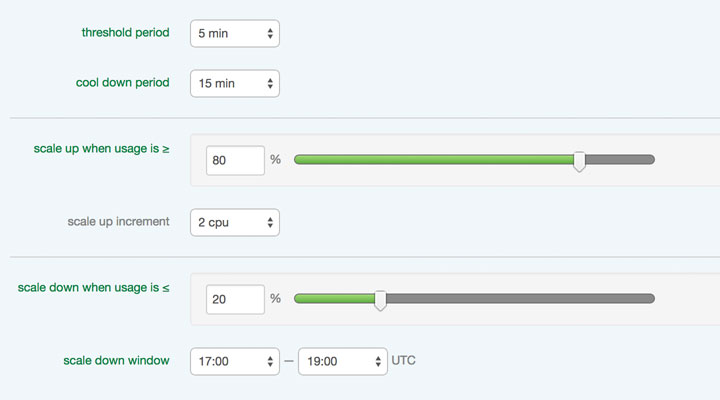
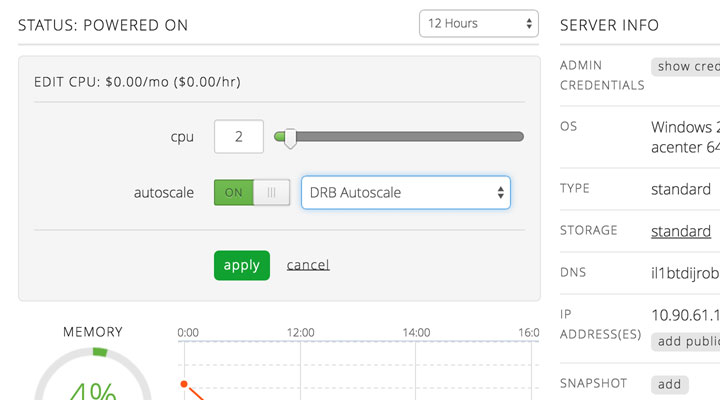
Vertical autoscaling (scaling up/down) adds (or removes) CPUs to (or from) an existing server based on the policy thresholds set. This policy gets applied on a server by server basis. See details below on when servers are scaled up or down for more information on what triggers a vertical Autoscale event. Horizontal autoscaling (scaling out/in) powers on (or off) servers within a group and adds (or removes) them from the load balancer configuration based on the thresholds set in the policy. This policy is applied at the group level and will affect every server within the group. See details below on when servers are scaled out or in for more information on what triggers a horizontal Autoscale event.
Can I use both vertical and horizontal Autoscale on the same server(s)?
Though it is not explicitly disabled by the platform, it is not recommended that you use both options in conjunction with each other (i.e. servers with vertical Autoscale policies inside a server group with a horizontal Autoscale policy). While this case should not cause anything to break, it can result in unpredictable behavior. (In one case, for example, if a horizontal Autoscale policy scales down, it may turn off a server that had a vertical Autoscale policy configured on it.)
How soon do changes to Autoscale policies take effect on any servers that use it?
A policy takes effect instantly.
How often are virtual machines sampled for utilization data points?
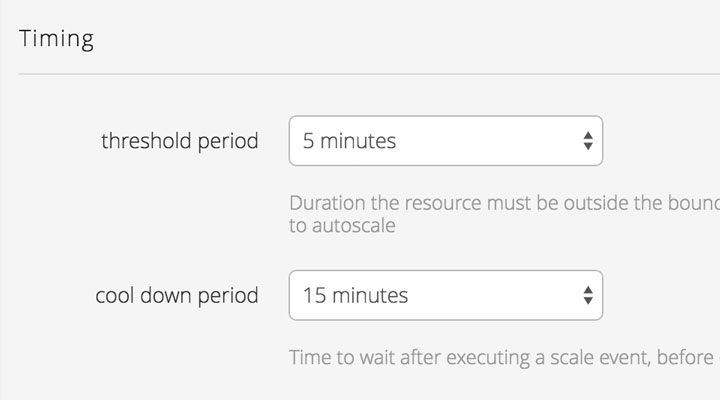
While the minimum threshold period for an Autoscale policy is 5 minutes, the Lumen Cloud platform collects data points far more frequently for each server. In fact, each 5 minute threshold period contains hundreds of data points. This ensures that your server scales because of an overall utilization trend, not just an isolated spike in utilization over a few seconds.